Regular ICS in mild asthma
Regular ICS has been shown to achieve asthma control in patients with mild asthma1
• 5-minute read
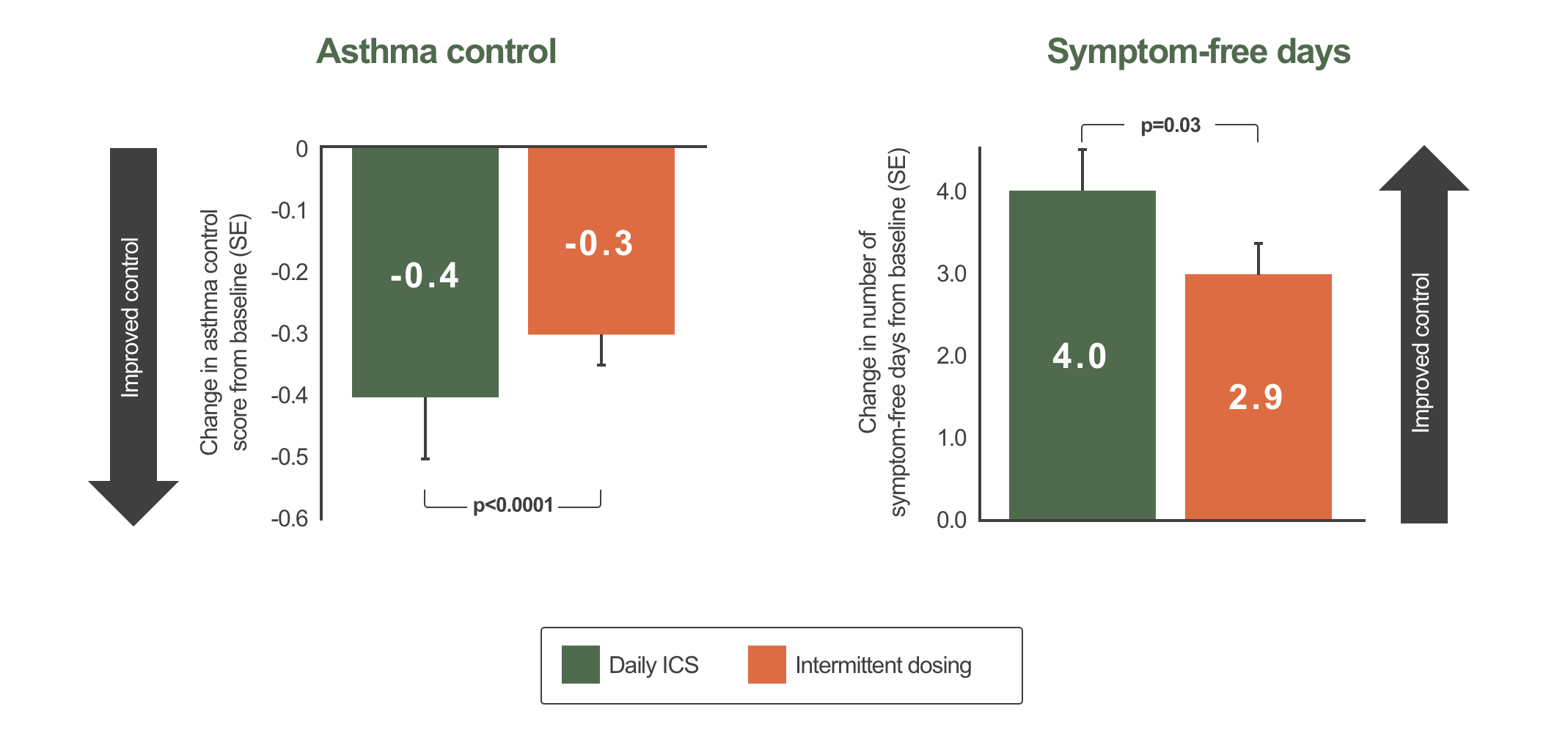
Increased asthma control and symptom free days in patients with mild asthma treated with regular vs intermittent ICS1*
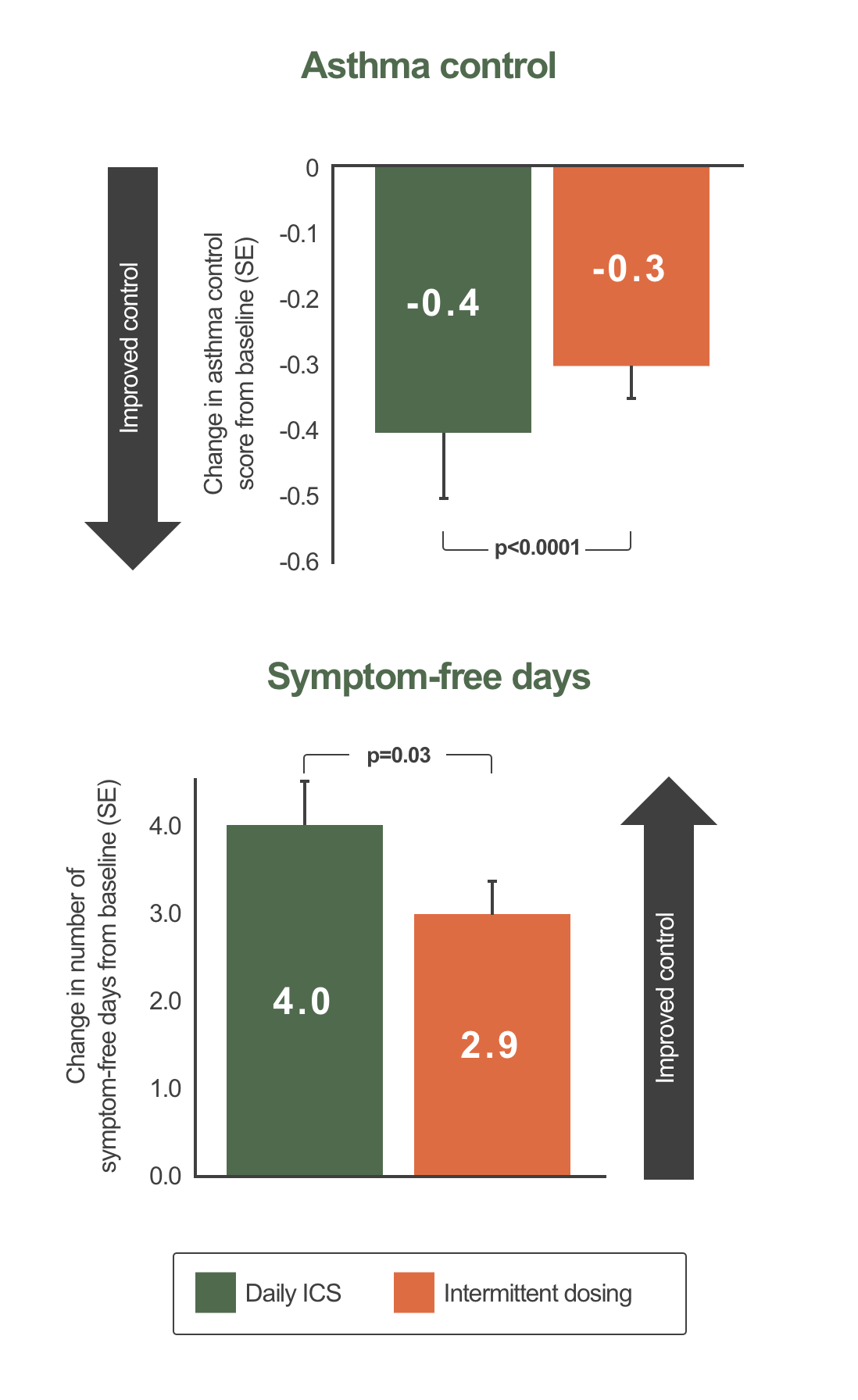
1-year, parallel-group, randomized, double-blind study (n with mild asthma =225; 18–65 years). Patients were assigned to one of three parallel treatment groups: 200 μg bid BUD with oral placebo(n=73), 20 mg bid oral zafirlukast with inhaled placebo (n=76), or bid oral and inhaled placebo (n=76; intermittent treatment). All arms also used 800 μg bid BUD in response to symptom worsening. All treatments were well tolerated. Only data for daily ICS and placebo arms are shown. This graph has been independently created by GSK from the original data pubilshed in Boushey H, et al. N Engl J Med 2005;352:1519–28.
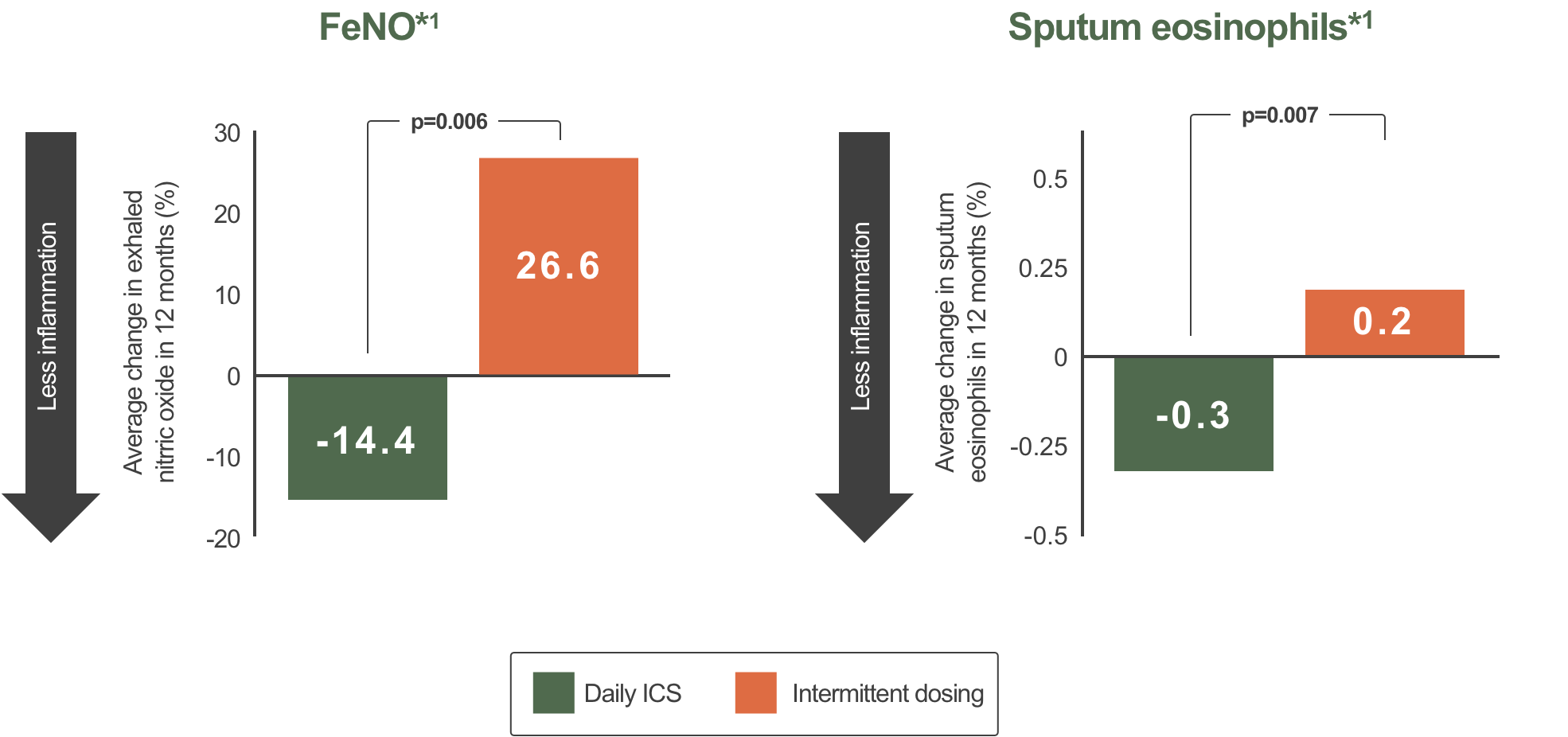
Markers of eosinophilic inflammation are reduced using regular high-dose ICS
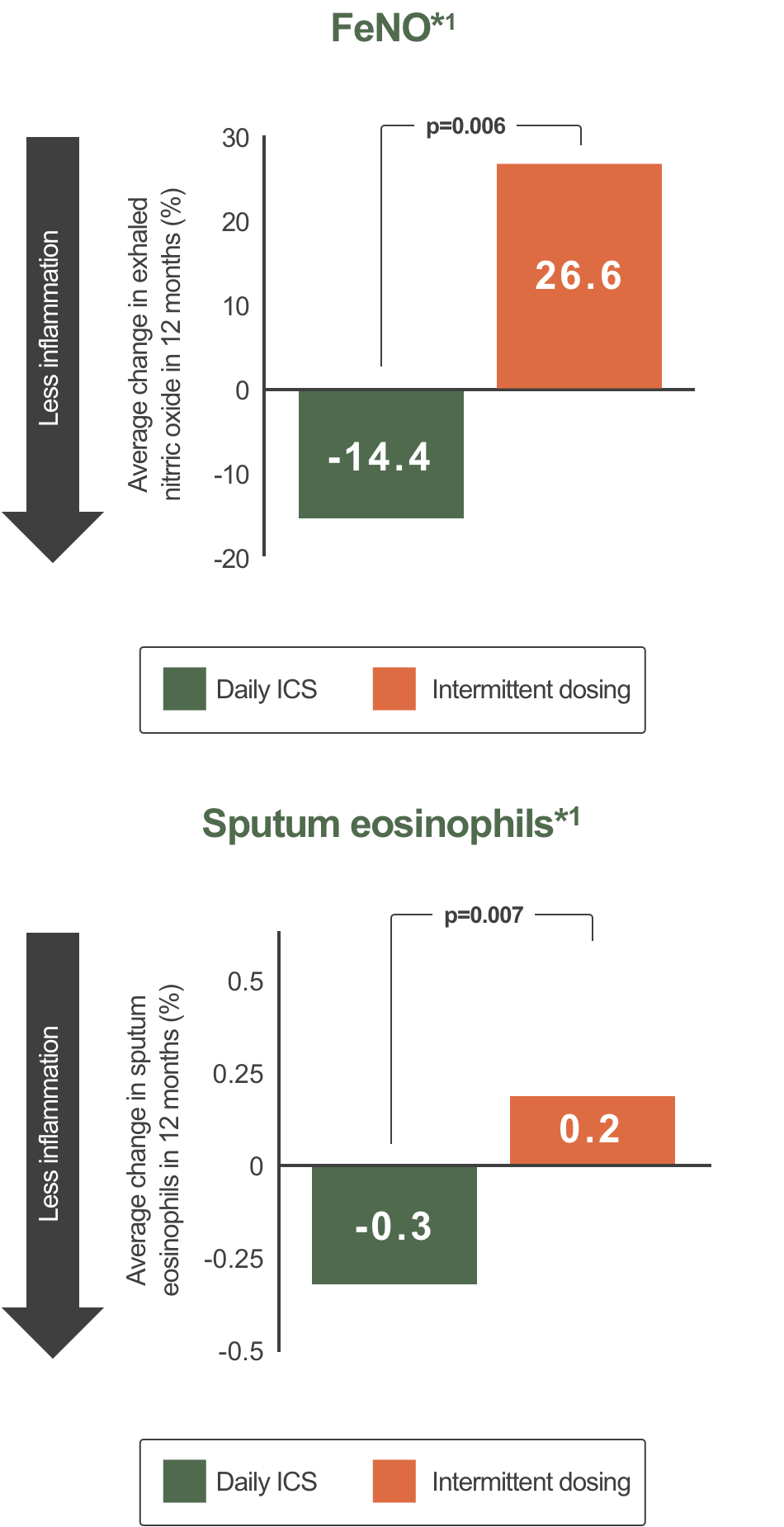
*1-year, parallel-group, randomized, double-blind study (n with mild asthma =225; 18–65 years) . Patients were assigned to one of three parallel treatment groups: 200 μg bid BUD with oral placebo (n=73), 20 mg bid oral zafirlukast with inhaled placebo (n=76), or bid oral and inhaled placebo (n=76; intermittent treatment). All arms also used 800 μg bid BUD in response to symptom worsening. All treatments were well tolerated. Only data for daily ICS and placebo arms are shown. This graph has been independently created by GSK from the original data pubilshed in Boushey H, et al. N Engl J Med 2005;352:1519–28.
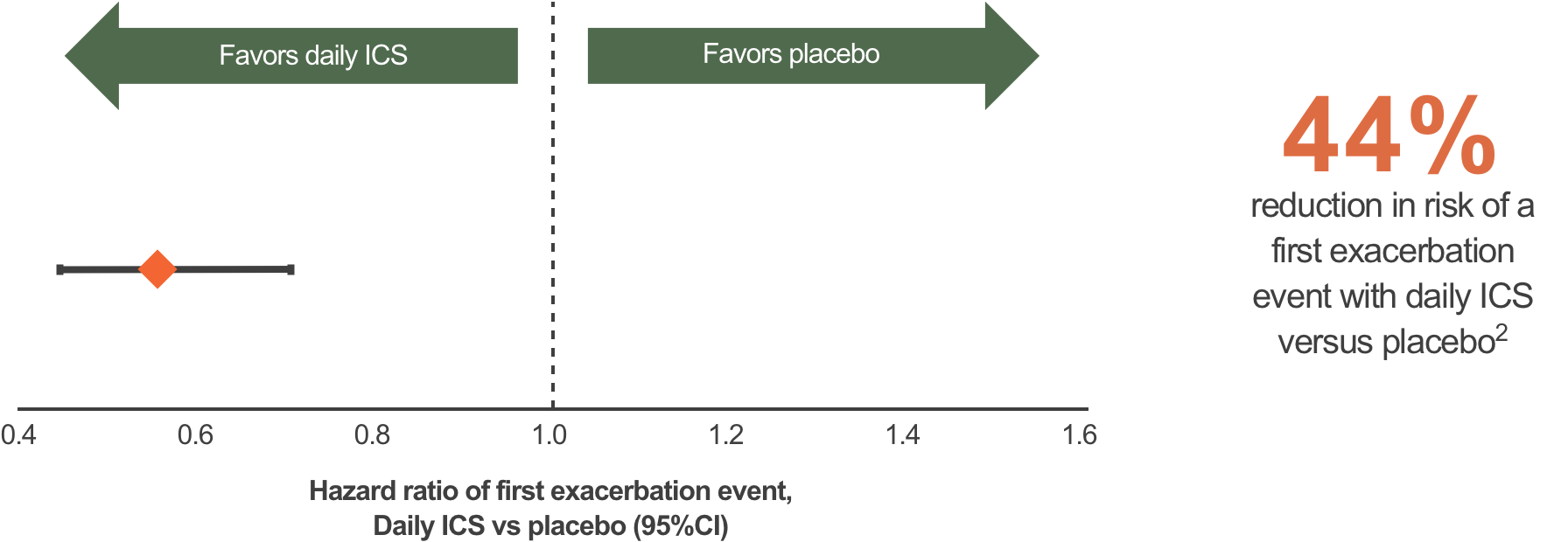
Early and regular treatment with ICS improves lung function and prevents exacerbations in mild asthma2†

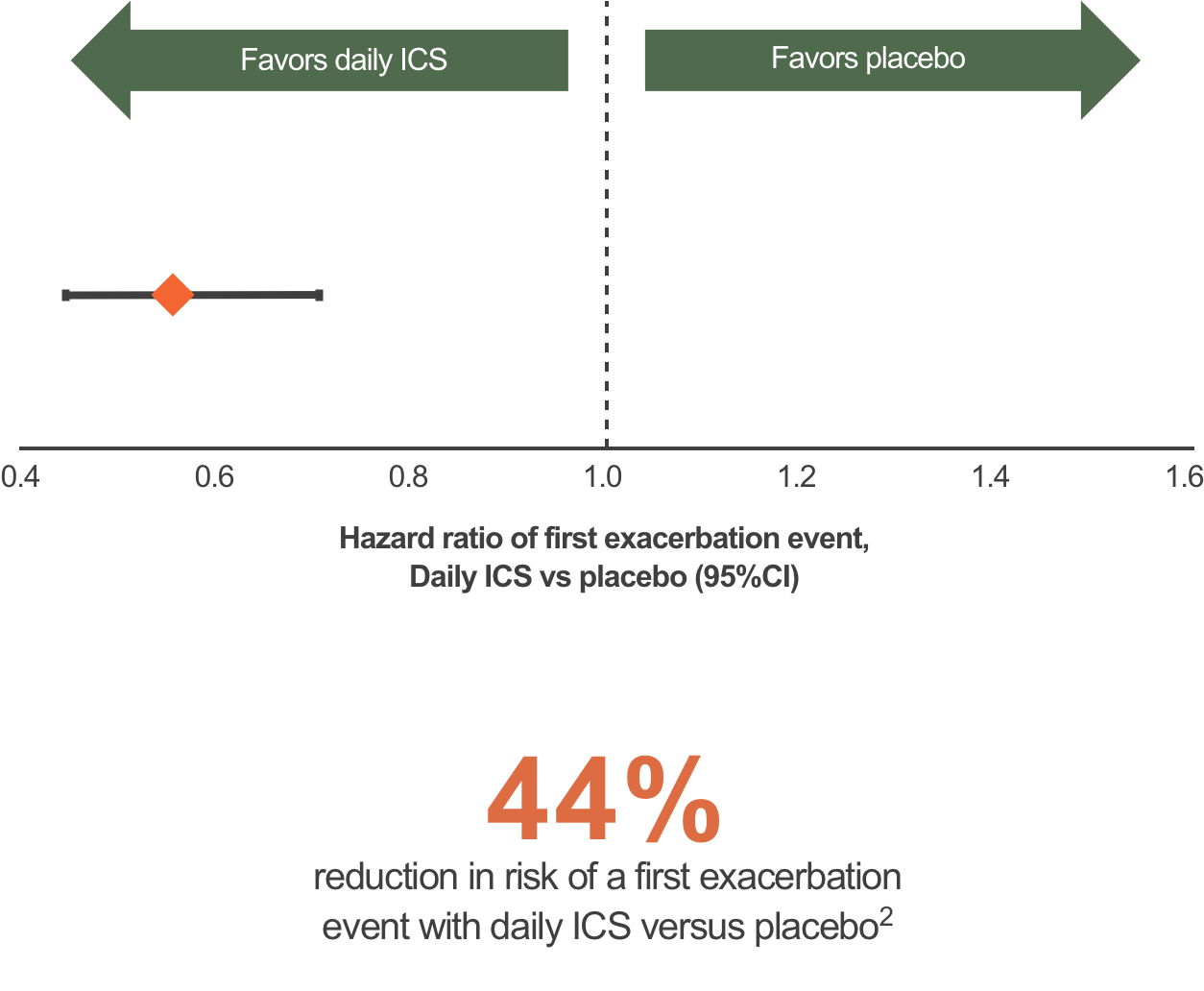
†3-year, parallel-group, randomized, double-blind study (n with mild asthma =7165; 5–66 years) designed to compare the effects of BUD 400 μg qd (200 μg qd aged ≤11 years) (n=3597) with lactose placebo qd (n=3568) on lung function and exacerbations. Both treatments were well tolerated. These graphs have been independently created by GSK from the original data pubilshed in Pauwels RA, et al. Lancet 2003;361:1071–6.
In patients with mild asthma, regular ICS:




*Regular ICS compared to intermittent active therapy; †Regular ICS compared to placebo
GINA, Global Initiative for Asthma; HCP, healthcare professional; ICS, inhaled corticosteroid; LABA, long-acting β2-agonist; LTRA, leukotriene receptor antagonist; MART, maintenance and reliever therapy; SABA, short-acting β2-agonist.
References
1. Boushey H, et al. N Engl J Med 2005;352:1519–28;
2. Pauwels RA, et al. Lancet 2003;361:1071–6.
NX-GBL-ASU-WCNT-220009 | March 2023
Related media
Continue your learning with these related resources
 Infographic
Infographic
 Infographic
Infographic
 Infographic
Infographic
 Case Study
Case Study